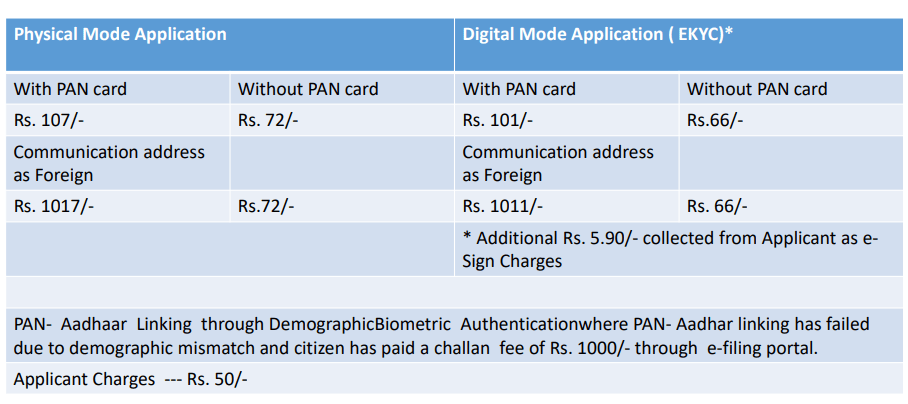
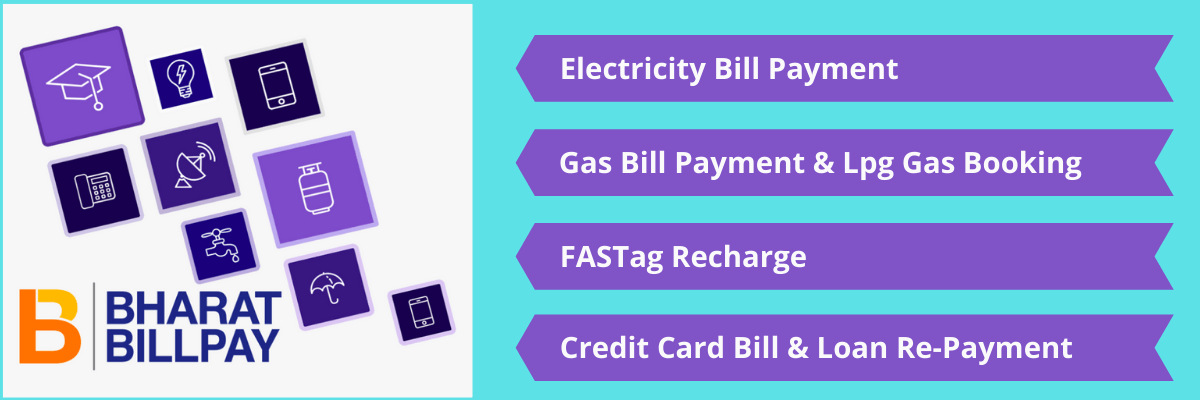
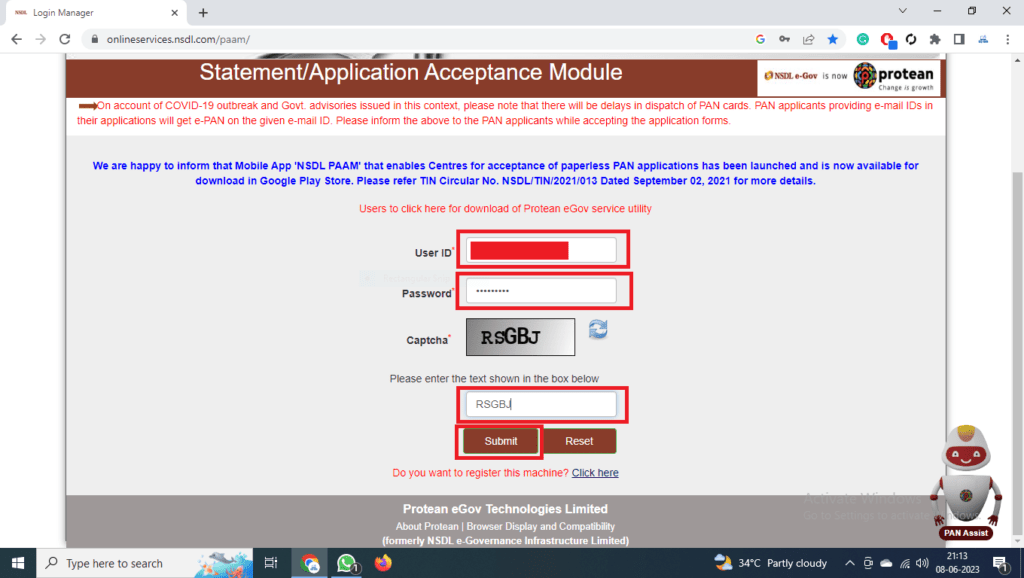
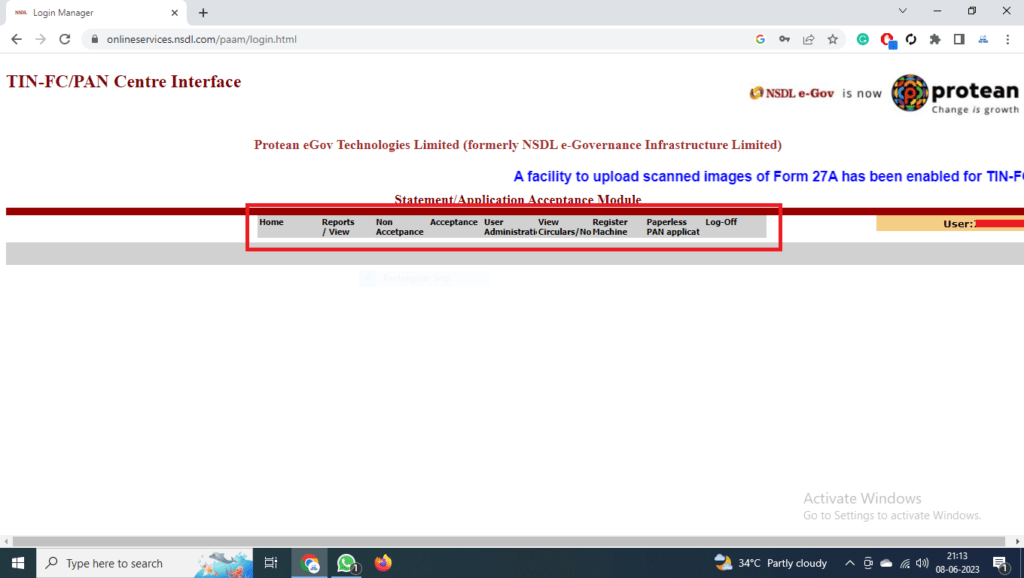
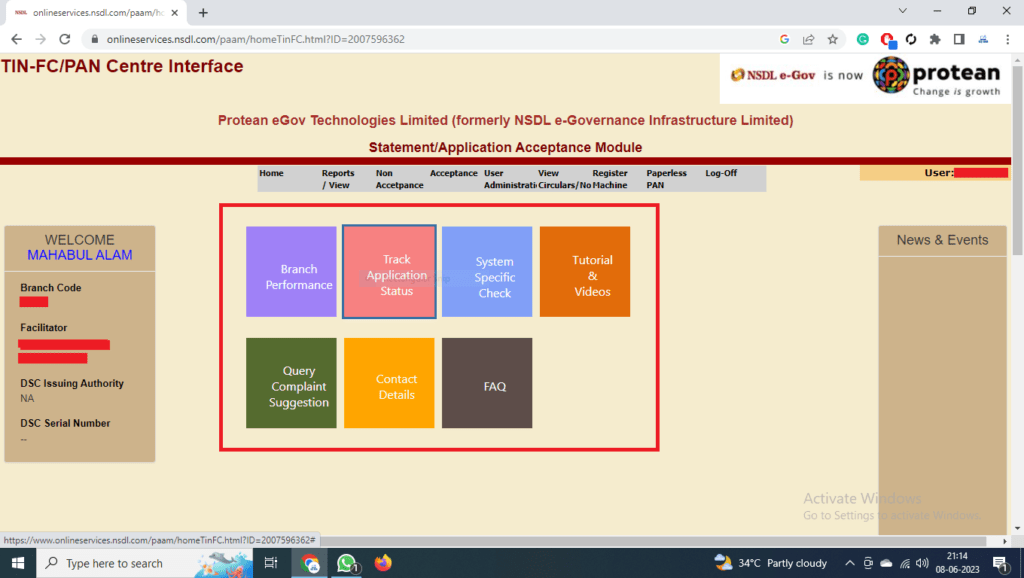
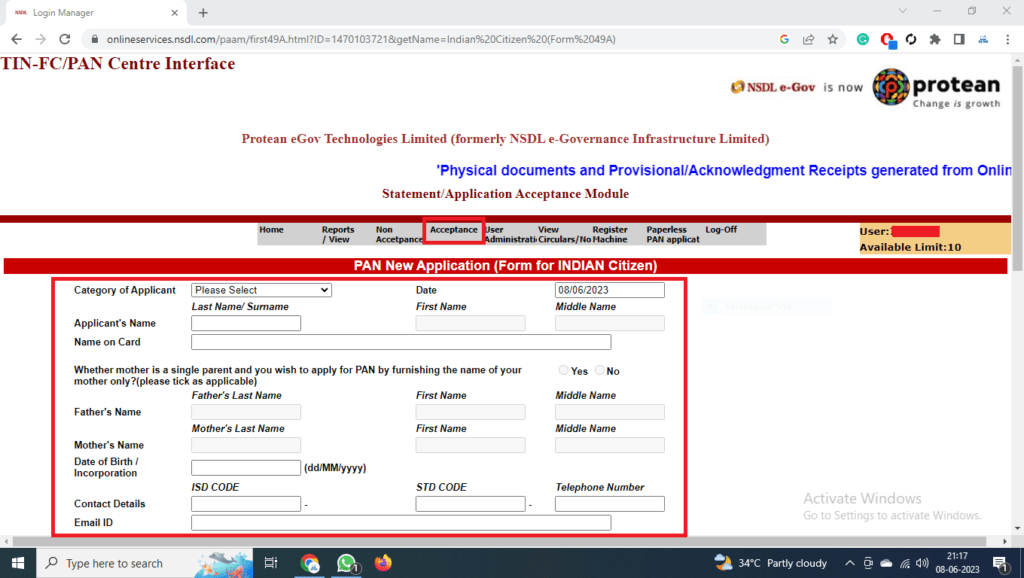
| 1 | ACT Broadband | BroadBand |
| 2 | Asianet | BroadBand |
| 3 | Comway Broadband | BroadBand |
| 4 | Connect Broadband | BroadBand |
| 5 | Den | BroadBand |
| 6 | Fusionnet | BroadBand |
| 7 | Hathway Broadband | BroadBand |
| 8 | INSTALINKS | BroadBand |
| 9 | Instanet Broadband | BroadBand |
| 10 | ION | BroadBand |
| 11 | Netplus Broadband | BroadBand |
| 12 | Nextra Broadband | BroadBand |
| 13 | Spectranet Broadband | BroadBand |
| 14 | Tikona Broadband | BroadBand |
| 15 | Timbl Broadband | BroadBand |
| 16 | TTN Broadband | BroadBand |
| 17 | Vfibernet Broadband | BroadBand |
| 18 | Adani Electricity | ElectriCity |
| 19 | Ajmer Vidyut Vitran Nigam Limited | ElectriCity |
| 20 | APDCL (Non-RAPDR) – ASSAM | ElectriCity |
| 21 | APDCL (RAPDR) – ASSAM | ElectriCity |
| 22 | APEPDCL – Andhra Pradesh | ElectriCity |
| 23 | APSPDCL – Andhra Pradesh | ElectriCity |
| 24 | Bangalore Electricity supply company Ltd | ElectriCity |
| 25 | BEST Undertaking | ElectriCity |
| 26 | Bhagalpur Electricity Distribution Company P Ltd | ElectriCity |
| 27 | Bharatpur Electricity Services Ltd | ElectriCity |
| 28 | Bikaner Electricity Supply Limited | ElectriCity |
| 29 | BSES Rajdhani Power Limited | ElectriCity |
| 30 | BSES Rajdhani Prepaid Meter Recharge | ElectriCity |
| 31 | BSES Yamuna Power Limited | ElectriCity |
| 32 | BSES Yamuna Prepaid Meter Recharge | ElectriCity |
| 33 | Calcutta Electric Supply Corporation Limited | ElectriCity |
| 34 | Central Power Distribution Corporation Ltd. of Andhra Pradesh APCPDCL | ElectriCity |
| 35 | Chamundeshwari Electricity Supply Corp Ltd (CESCOM) | ElectriCity |
| 36 | Chhattisgarh State Power Distribution Company Ltd | ElectriCity |
| 37 | Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu Power Distribution Corporation Limited | ElectriCity |
| 38 | Dakshin Gujarat Vij Company Limited | ElectriCity |
| 39 | Dakshin Haryana Bijli Vitran Nigam | ElectriCity |
| 40 | Dakshinanchal Vidyut Vitran Nigam Limited DVVNL Postpaid and Smart Prepaid Meter Recharge | ElectriCity |
| 41 | Daman And Diu Electricity | ElectriCity |
| 42 | Department of Power Government of Arunachal Pradesh – Prepaid | ElectriCity |
| 43 | Department of Power Nagaland | ElectriCity |
| 44 | Department of Power, Government of Arunachal Pradesh | ElectriCity |
| 45 | DNH Power Distribution Company Limited | ElectriCity |
| 46 | DNHPDCL – DADRA AND NAGAR HAVELI | ElectriCity |
| 47 | Electricity Department Chandigarh | ElectriCity |
| 48 | Gift Power Company Limited | ElectriCity |
| 49 | Goa Electricity Department | ElectriCity |
| 50 | Government of Puducherry Electricity Department | ElectriCity |
| 51 | Gulbarga Electricity Supply Company Limited | ElectriCity |
| 52 | Himachal Pradesh State Electricity Board Ltd | ElectriCity |
| 53 | Hubli Electricity Supply Company Ltd | ElectriCity |
| 54 | Hukkeri Rural Electric CoOperative Society Ltd | ElectriCity |
| 55 | India Power – WEST BENGAL | ElectriCity |
| 56 | Jaipur Vidyut Vitran Nigam | ElectriCity |
| 57 | Jammu and Kashmir Power Development Department | ElectriCity |
| 58 | Jamshedpur Utilities & Services (JUSCO) | ElectriCity |
| 59 | Jharkhand Bijli Vitran Nigam Limited | ElectriCity |
| 60 | Jharkhand Bijli Vitran Nigam Limited – Prepaid Meter Recharge | ElectriCity |
| 61 | Jodhpur Vidyut Vitran Nigam Limited | ElectriCity |
| 62 | Kannan Devan Hills Plantations Company Private Limited | ElectriCity |
| 63 | Kanpur Electricity Supply Company | ElectriCity |
| 64 | Kerala State Electricity Board Ltd | ElectriCity |
| 65 | Kota Electricity Distribution Limited | ElectriCity |
| 66 | Lakshadweep Electricity Department | ElectriCity |
| 67 | Madhya Gujarat Vij Company Limited | ElectriCity |
| 68 | Madhya Kshetra Vitaran (Rural) – Madhya Pradesh | ElectriCity |
| 69 | Madhya Kshetra Vitaran (Urban) – Madhya Pradesh | ElectriCity |
| 70 | Madhyanchal Vidyut Vitran Nigam Limited MVVNL Postpaid and Smart Prepaid Meter Recharge | ElectriCity |
| 71 | Mangalore Electricity Supply Co. Ltd MESCOM | ElectriCity |
| 72 | Mangalore Electricity Supply Company LTD – Non RAPDR | ElectriCity |
| 73 | Meghalaya Power Dist Corp Ltd | ElectriCity |
| 74 | MePDCL Smart Prepaid Meter Recharge | ElectriCity |
| 75 | MSEDCL | ElectriCity |
| 76 | Muzaffarpur Vidyut Vitran | ElectriCity |
| 77 | NESCO Utility | ElectriCity |
| 78 | New Delhi Municipal Council (NDMC) | ElectriCity |
| 79 | Noida Power Copmpany Limited | ElectriCity |
| 80 | North Bihar Power Distribution Co. Ltd | ElectriCity |
| 81 | Paschim Gujarat Vij Company Limited | ElectriCity |
| 82 | Paschim Kshetra Vidyut Vitaran – Madhya Pradesh | ElectriCity |
| 83 | Paschimachal Vidyut Vitran Nigam Limited | ElectriCity |
| 84 | Poorv Kshetra Vitaran (NBG-Urban) – MADHYA PRADESH | ElectriCity |
| 85 | Poorv Kshetra Vitaran (Rural) – MADHYA PRADESH | ElectriCity |
| 86 | Power And Electricity Department Mizoram | ElectriCity |
| 87 | Punjab State Power Corporation Limited | ElectriCity |
| 88 | Purvanchal Vidyut Vitran Nigam Limited – PUVVNL – Postpaid and Smart Prepaid Meter Recharge | ElectriCity |
| 89 | Sikkim Power RURAL | ElectriCity |
| 90 | Sikkim Power URBAN | ElectriCity |
| 91 | SNDL Power – NAGPUR | ElectriCity |
| 92 | South Bihar Power Distribution Co. Ltd | ElectriCity |
| 93 | Southern Electricity Supply Company Of Odisha Limited | ElectriCity |
| 94 | Spurt Electric Limited | ElectriCity |
| 95 | Tamil Nadu Electricity Board | ElectriCity |
| 96 | Tata Power – Mumbai | ElectriCity |
| 97 | Tata Power AJMER – RAJASTHAN | ElectriCity |
| 98 | Tata Power Delhi Distribution Limited | ElectriCity |
| 99 | Telangana Northern Power Distribution Company | ElectriCity |
| 100 | Telangana State Southern Power Distribution Company | ElectriCity |
| 101 | Thrissur Corporation Electricity Department | ElectriCity |
| 102 | Torrent Power Limited – Agra | ElectriCity |
| 103 | Torrent Power Limited – Ahmedabad | ElectriCity |
| 104 | Torrent Power Limited – Bhiwandi | ElectriCity |
| 105 | Torrent Power Limited – Surat | ElectriCity |
| 106 | TP Ajmer Distribution Ltd TPADL | ElectriCity |
| 107 | TP Central Odisha Distribution Limited (TPCODL) | ElectriCity |
| 108 | TP Renewables Microgrid Ltd | ElectriCity |
| 109 | TP Southen Odisha Distribution Ltd-Smart Prepaid Meter Recharge | ElectriCity |
| 110 | Tripura Electricity Corp Ltd | ElectriCity |
| 111 | Uttar Gujarat Vij Company Limited | ElectriCity |
| 112 | Uttar Haryana Bijli Vitran Nigam | ElectriCity |
| 113 | Uttar Haryana Bijli Vitran Nigam Limited Prepaid | ElectriCity |
| 114 | Uttar Pradesh Power Corporation Ltd (RURAL) | ElectriCity |
| 115 | Uttar Pradesh Power Corporation Ltd (Urban – Smart Meter) | ElectriCity |
| 116 | Uttarakhand Power Corporation Ltd – UPCL | ElectriCity |
| 117 | WESCO Utility | ElectriCity |
| 118 | West Bengal State Electricity Distribution Company Limited | ElectriCity |
| 119 | Western Electricity Supply Company Of Orissa Limited | ElectriCity |
| 120 | Axis Bank | FASTag |
| 121 | Bank of Baroda | FASTag |
| 122 | Equitas FASTag | FASTag |
| 123 | Federal Bank | FASTag |
| 124 | HDFC Bank | FASTag |
| 125 | ICICI Bank | FASTag |
| 126 | IDBI Bank | FASTag |
| 127 | IDFC First Bank | FASTag |
| 128 | Indian Highways Management Company | FASTag |
| 129 | IndusInd Bank | FASTag |
| 130 | Jammu and Kashmir Bank | FASTag |
| 131 | Kotak Mahindra Bank | FASTag |
| 132 | Paul Merchants | FASTag |
| 133 | Paytm Payments Bank | FASTag |
| 134 | UCO Bank | FASTag |
| 135 | Aavantika Gas Ltd | Gas |
| 136 | Assam Gas Company Limited | Gas |
| 137 | Bhagyanagar Gas Limited | Gas |
| 138 | Central U.P. Gas Limited | Gas |
| 139 | Charotar Gas Sahakari Mandali Ltd | Gas |
| 140 | GAIL Gas Limited | Gas |
| 141 | Green Gas Limited(GGL) | Gas |
| 142 | Gujarat Gas Limited | Gas |
| 143 | Haryana City Gas | Gas |
| 144 | Indian Oil-Adani Gas Private Limited | Gas |
| 145 | Indraprastha Gas Limited | Gas |
| 146 | IRM Energy Private Limited | Gas |
| 147 | Mahanagar Gas- Mumbai | Gas |
| 148 | Megha Gas | Gas |
| 149 | Sabarmati Gas Limited (SGL) | Gas |
| 150 | Sanwariya Gas Limited | Gas |
| 151 | Torrent Gas Moradabad Limited | Gas |
| 152 | Tripura Natural Gas | Gas |
| 153 | Unique Central Piped Gases Pvt Ltd (UCPGPL) | Gas |
| 154 | Aditya Birla Health Insurance Co Limited | Insurance |
| 155 | Aegon Life Insurance | Insurance |
| 156 | Aviva Life Insurance | Insurance |
| 157 | Bajaj Allianz General Insurance | Insurance |
| 158 | Bajaj Allianz Life Insurance | Insurance |
| 159 | Bharti Axa Life Insurance | Insurance |
| 160 | Canara HSBC Oriental Bank of Commerce Life Insurance | Insurance |
| 161 | DHFL Pramerica Life Insurance Co. Ltd | Insurance |
| 162 | Edelweiss Tokio Life Insurance | Insurance |
| 163 | Exide Life Insurance | Insurance |
| 164 | Future Generali India Life Insurance Company Limited | Insurance |
| 165 | HDFC Life Insurance Co. Ltd. | Insurance |
| 166 | ICICI Prudential Life Insurance | Insurance |
| 167 | IDBI federal Life Insurance | Insurance |
| 168 | INDIA FIRST Life Insurance | Insurance |
| 169 | Kotak Life Insurance Company Limited | Insurance |
| 170 | Life Insurance Corporation of India | Insurance |
| 171 | Magma HDI – Health Insurance | Insurance |
| 172 | Magma HDI – Life Insurance | Insurance |
| 173 | Magma HDI – Motor Insurance | Insurance |
| 174 | Max Bupa Health Insurance | Insurance |
| 175 | Max Life Insurance | Insurance |
| 176 | PNB Metlife | Insurance |
| 177 | Pramerica Life Insurance Limited | Insurance |
| 178 | Reliance General Insurance Company Limited | Insurance |
| 179 | Reliance Nippon Life Insurance | Insurance |
| 180 | Royal Sundaram General Insurance Co. Limited | Insurance |
| 181 | SBI Life Insurance | Insurance |
| 182 | SBIG | Insurance |
| 183 | Shriram General Insurance | Insurance |
| 184 | Shriram Life Insurance Co Ltd | Insurance |
| 185 | Star Union Dai Ichi Life Insurance | Insurance |
| 186 | Tata AIA Life Insurance | Insurance |
| 187 | Vastu Housing Finance Corporation Limited | Insurance |
| 188 | Airtel(LL) | LandLine |
| 189 | BSNL – Corporate | LandLine |
| 190 | BSNL Individual(LL) | LandLine |
| 191 | MTNL – Delhi(LL) | LandLine |
| 192 | MTNL – Mumbai(LL) | LandLine |
| 193 | Tata TeleServices (CDMA) | LandLine |
| 194 | Aavas Financiers | Loan |
| 195 | Adani Housing Finance | Loan |
| 196 | Aditya Birla Finance ltd. (ABFL) | Loan |
| 197 | Aditya Birla Housing Finance Limited | Loan |
| 198 | Agora Microfinance India Ltd – AMIL | Loan |
| 199 | Altum Credo Home Finance | Loan |
| 200 | Annapurna Finance Private Limited-MSME | Loan |
| 201 | Arohan Financial Services Limited | Loan |
| 202 | Ascend Capital | Loan |
| 203 | Aspire Home Finance | Loan |
| 204 | Avail | Loan |
| 205 | Avanse Financial Services Ltd | Loan |
| 206 | Axis Bank Limited-Microfinance | Loan |
| 207 | Baid Leasing and Finance | Loan |
| 208 | Bajaj Auto Finance | Loan |
| 209 | Bajaj Finserv | Loan |
| 210 | BERAR Finance Limited | Loan |
| 211 | Bharat Financial Inclusion Ltd | Loan |
| 212 | Capri Global Capital Limited | Loan |
| 213 | Capri Global Housing Finance | Loan |
| 214 | Chaitanya India Fin Credit Pvt Ltd | Loan |
| 215 | Clix | Loan |
| 216 | Credit Wise Capital | Loan |
| 217 | CreditAccess Grameen – Microfinance | Loan |
| 218 | CreditAccess Grameen – Retail Finance | Loan |
| 219 | DCB Bank Loan Repayment | Loan |
| 220 | Digamber Capfin Limited | Loan |
| 221 | DMI Finance | Loan |
| 222 | Dvara Kshetriya Gramin Financials Private Limited | Loan |
| 223 | Eduvanz Financing Pvt. Ltd. | Loan |
| 224 | ESS KAY FINCORP | Loan |
| 225 | Faircent | Loan |
| 226 | Fincare Small Finance Bank | Loan |
| 227 | FlexiLoans | Loan |
| 228 | FlexSalary | Loan |
| 229 | Hero FinCorp | Loan |
| 230 | Hiranandani Financial Services Pvt Ltd | Loan |
| 231 | Home Credit India Finance Pvt. Ltd | Loan |
| 232 | Home First Finance Company India Limited | Loan |
| 233 | I2I Funding | Loan |
| 234 | ICICI Bank Ltd – Loans | Loan |
| 235 | IDFC First Bank Limited | Loan |
| 236 | IIFL Finance Limited | Loan |
| 237 | IIFL Home Finance | Loan |
| 238 | India Home Loan Limited | Loan |
| 239 | India Shelter Finance Corporation Limited | Loan |
| 240 | Indiabulls Consumer Finance Limited | Loan |
| 241 | INDIABULLS HOUSING FINANCE | Loan |
| 242 | INDUSIND BANK – CFD | Loan |
| 243 | Jain Motor Finmart | Loan |
| 244 | Jana Small Finance Bank | Loan |
| 245 | Janakalyan Financial Services Private Limited | Loan |
| 246 | John Deere Financial India Private Limited | Loan |
| 247 | Kanakadurga Finance Limited | Loan |
| 248 | Khush Housing Finance Pvt Ltd | Loan |
| 249 | Kinara Capital | Loan |
| 250 | Kissht | Loan |
| 251 | Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd.-Loans | Loan |
| 252 | Kotak Mahindra Prime Limited | Loan |
| 253 | L&T Finance Limited | Loan |
| 254 | L&T Housing Finance | Loan |
| 255 | Light Microfinance Private Limited | Loan |
| 256 | LoanTAP | Loan |
| 257 | LokSuvidha | Loan |
| 258 | Mahaveer Finance India Limited | Loan |
| 259 | Mahindra and Mahindra Financial Services Limited | Loan |
| 260 | Mahindra Rural Housing Finance | Loan |
| 261 | Manappuram Finance Limited-Vehicle Loan | Loan |
| 262 | Maxvalue Credits And Investments Ltd | Loan |
| 263 | Midland Microfin Ltd | Loan |
| 264 | Mintifi Finserve Private Limited | Loan |
| 265 | Motilal Oswal Home Finance | Loan |
| 266 | Muthoot Finance | Loan |
| 267 | Muthoot Fincorp Ltd | Loan |
| 268 | Nagar Nigam Aligarh- muncipality | Loan |
| 269 | Netafim Agricultural Financing Agency Pvt. Ltd. | Loan |
| 270 | Nidhilakshmi Finance | Loan |
| 271 | NM Finance | Loan |
| 272 | OHMYLOAN | Loan |
| 273 | OMLP2P.COM | Loan |
| 274 | Oroboro | Loan |
| 275 | PaisaDukan | Loan |
| 276 | Pooja Finelease | Loan |
| 277 | Samasta Microfinance Limited | Loan |
| 278 | SHRIRAM CITY UNION FINANCE LIMITED | Loan |
| 279 | Shriram Housing Finance Limited | Loan |
| 280 | SMEcorner | Loan |
| 281 | Snapmint | Loan |
| 282 | StashFin | Loan |
| 283 | Svatantra Microfin Private Limited | Loan |
| 284 | Tata Capital Financial Services Limited | Loan |
| 285 | Tata Capital Housing Finance Limited | Loan |
| 286 | TVS Credit | Loan |
| 287 | Ujjivan Small Finance Bank | Loan |
| 288 | Varthana | Loan |
| 289 | Vistaar Financial services Private Limited | Loan |
| 290 | ZestMoney | Loan |
| 291 | Bharat Gas | LPG |
| 292 | HP Gas | LPG |
| 293 | Indane Gas | LPG |
| 294 | Google Play Recharge | PlayCode |
| 295 | Ahmedabad Municipal Corporation | Water |
| 296 | Bangalore Water Supply and Sewerage Board (BWSSB) | Water |
| 297 | Bhopal Municipal Corporation | Water |
| 298 | Delhi Development Authority (DDA) | Water |
| 299 | Delhi Jal Board | Water |
| 300 | Department of Public Health Engineering-Water, Mizoram | Water |
| 301 | Greater Warangal Municipal Corporation | Water |
| 302 | Gwalior Municipal Corporation | Water |
| 303 | Haryana Urban Development Authority | Water |
| 304 | Hyderabad Metropolitan Water Supply and Sewerage Board (HMWSSB) | Water |
| 305 | Indore Municipal Corporation | Water |
| 306 | Jabalpur Municipal Corporation | Water |
| 307 | Jalkal Vibhag Nagar Nigam Prayagraj | Water |
| 308 | Kalyan Dombivali Municipal Corporation | Water |
| 309 | Kerala Water Authority (KWA) | Water |
| 310 | Madhya Pradesh Urban (e-Nagarpalika) | Water |
| 311 | Municipal Corporation Chandigarh | Water |
| 312 | Municipal Corporation Jalandhar | Water |
| 313 | Municipal Corporation Ludhiana | Water |
| 314 | Municipal Corporation of Amritsar | Water |
| 315 | Municipal Corporation of Gurugram (MCG) | Water |
| 316 | Mysuru City Corporation | Water |
| 317 | Nagar Nigam Aligarh | Water |
| 318 | New Delhi Municipal Council (NDMC) | Water |
| 319 | Public Health Engineering Department, Haryana | Water |
| 320 | Pune Municipal Corporation | Water |
| 321 | Punjab Municipal Corporation/Council | Water |
| 322 | Ranchi Municipal Corporation | Water |
| 323 | Silvassa Municipal Council | Water |
| 324 | Surat Municipal Corporation | Water |
| 325 | Ujjain Nagar Nigam � PHED | Water |
| 326 | Urban Improvement Trust (UIT) – Bhiwadi | Water |
| 327 | Uttarakhand Jal Sansthan | Water |